1. Product description
Parallel pins serve the purpose of friction-locking and positional securing connection of components and are particularly suitable for applications that are never or only very rarely loosened. Parallel pins according to DIN EN ISO 2338 are precision-manufactured, cylindrical fastening elements without threads, primarily used for positioning and connecting/fixing two or more parts in, for example, machines, furniture, or various devices. They are an effective solution to ensure precise alignment between parts while enabling reliable and easy assembly.
2. Product details
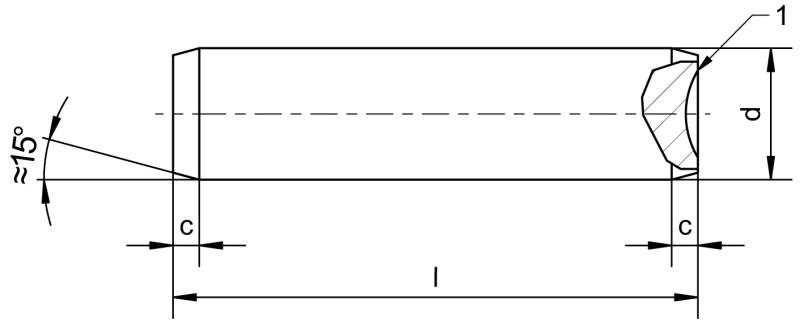
Size: 0,6 h8 x 2 - 50 m6 x 200
d: 0,6 - 50
l: 2 - 200
l min: 1,75 - 199,25
l max: 2,25 - 200,75
c ≈: 0,2 - 8
Material group: Steel, stainless steel, stainless steel A4 quality
Surface: bright, surface roughness Ra ≤ 0,8 µm or Ra ≤ 1,6 µm
3. Application Areas & Compatibility
Mechanical engineering: In mechanical engineering, they are often used to precisely position and secure machine parts. Their role is crucial in the manufacture of machine tools, pumps, gearboxes, and other mechanical devices where precise alignment is critical for functionality.
Electrical engineering: In electrical engineering, parallel pins are used to fix components within electrical devices such as motors, generators, and switchgear. They help ensure a permanent and secure assembly of these sensitive parts.
Precision instruments: In the manufacture of precision instruments, such as watches, measuring devices, or optical instruments, parallel pins are indispensable. They enable highly accurate assembly, which is essential for the precise functioning of these devices.
Medical technology: In medical technology, parallel pins are used in the manufacture of medical instruments, devices, and even implants. Their reliability and accuracy support the strict demands of this field for precision and durability.
Furniture industry: Parallel pins are also used in the furniture industry, such as for the assembly and alignment of fittings or hinges. Their easy installation and durability make them ideal for many applications in this area.
This wide applicability is partly due to the compatibility of parallel pins with various materials and construction techniques. Their universal design makes them a flexible solution for a variety of connection tasks in many different fields of application.
4. Advantages and Benefits
Precise positioning: One of the main strengths of parallel pins lies in their ability to ensure extremely accurate alignment between joined parts. This is crucial in applications where the exact position of components is essential for the correct functioning of the entire system.
High compatibility: Parallel pins can be used with a variety of materials and in different environments. They are compatible with metals, plastics, and composites, significantly increasing their application flexibility in design and manufacturing projects.
Easy Assembly and disassembly: The installation of parallel pins is generally straightforward and does not require special tools or skills, which helps reduce assembly times and associated costs. Additionally, they allow for easy disassembly for maintenance or repair work.
Reliability and durability: Parallel pins provide a robust and durable connection between components, which remains reliable even under load. Their design and material (steel, stainless steel, stainless steel A4 quality) ensure excellent resistance to mechanical stress and environmental influences.
Cost-effectiveness: Despite their high precision and reliability, parallel pins are a cost-effective solution for many mechanical fastening and positioning tasks. Standardization according to DIN EN ISO 2338 facilitates procurement and reduces storage costs through the use of standardized components.
Versatility in applications: The wide range of available sizes and materials allows the use of parallel pins in various applications, from highly precise medical instruments to heavy machinery.
Safety: Due to standardized manufacturing and precise fit, parallel pins also contribute to safety in the use of the end products. Correct assembly and adherence to tolerance specifications minimize the risk of assembly errors that could lead to failures or accidents.
Overall, parallel pins according to DIN EN ISO 2338 offer a combination of precision, reliability, and cost-efficiency, making them a preferred choice for many technical and industrial applications.
5. Assembly and Installation
Step 1 - Preparation of components: Before beginning assembly, ensure that the holes in the parts to be connected are clean, free of foreign substances, and drilled exactly according to the specifications of the parallel pins. The precision of the drilling directly influences the fit and performance of the connection.
Step 2 - Choosing the right fit: The fit between the parallel pin and the borehole is crucial for the connection's performance. There are different types of fits (e.g., interference fit, transition fit) that should be selected based on the application and requirements of the connection. An interference fit results in a firm, permanent connection, whereas a transition fit allows for positioning with slight adjustability.
Step 3 - Assembly tools and techniques: For the installation of parallel pins, soft hammers or hydraulic presses may be needed, especially for interference fits. The choice of the right tool depends on the size of the parallel pin and the intended purpose. It is important to apply even pressure to avoid distortions or damage to the parts.
Step 4 - Securing measures: In some applications, it may be necessary to take additional securing measures to prevent the parallel pin from loosening under operating conditions. Options include using adhesives or locking wires, depending on the specific application requirements.
Step 5 - Inspection and testing: After assembly, it is important to check the correct installation to ensure that the fit and alignment of the components meet specifications. A thorough inspection can help identify and correct assembly errors before the assembly is put into operation.
Maintenance: Although parallel pins are known for their durability and reliability, regular inspections as part of maintenance work can help identify potential problems early and extend the lifespan of the assembly.
6. Safety instructions & Standards
Compliance with standards: Parallel pins according to DIN EN ISO 2338 comply with specific standards that define dimensions, materials, and tolerances. Adhering to these standards ensures that the parallel pins meet technical requirements and are suitable for the intended application. For the safety and reliability of the connection, it is essential to use only standard-compliant products.
Avoiding overload: Parallel pins are designed for specific loads. Overloading due to excessive mechanical forces can damage the pins or lead to their failure.
Dealing with corrosion: In environments prone to corrosion, parallel pins made from corrosion-resistant materials should be used, or appropriate protective measures should be taken. Corrosion can weaken the integrity of the connection and pose a safety risk.
Overview of various standards: Unhardened parallel pins are standardized according to EN ISO 2338, formerly DIN 7. The hardened version can be found in the EN ISO 8734, formerly DIN 6325. Another hardened variant with additional internal threading is standardized in DIN EN ISO 8735.
7. Custom-made products, Accessories and Extensions
At mbo Osswald, custom manufacturing of parallel pins to your exact specifications is possible. If a DIN-compliant parallel pin does not meet your specific requirements, we offer tailor-made special parts. We develop the required component specifically for your application or manufacture according to your drawing, utilizing the extensive material selection of our standard parts. We are able to make and implement almost any design change.
If you already have a drawing of your desired part or would like to develop a solution together with us, do not hesitate to contact mbo Osswald directly. We are ready to bring your ideas to life.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What are parallel pins used for?
What are the different standards for parallel pins?
What are parallel pins according to DIN EN ISO 2338?
What sizes of parallel pins are available?
What materials are used to manufacture parallel pins?
What surface roughness do the parallel pins have?
Why are parallel pins important in medical technology?
What are the advantages of parallel pins?
What considerations are important when installing parallel pins?
How does compliance with standards contribute to safety?
What should be considered when selecting materials and dealing with corrosion?
Are parallel pins also custom-made to measure?
Yes, at mbo Osswald, custom-made parallel pins are possible according to your wishes. If a DIN-compliant parallel pin does not meet your specific requirements, we offer you tailor-made special parts. We develop the required component specifically for your application or manufacture according to your drawing, using the extensive material selection of our standard parts. We are able to make and implement almost any constructive change.
If you already have a drawing of your desired part or want to develop a solution together with us, do not hesitate to directly contact mbo Osswald. We are ready to bring your ideas to life.