1. Product description
In the complex assembly of mechanical structures, set collars DIN 705 emerge as fundamental components to ensure stabilization and precise positioning of parts. These rings hold a shaft firmly, serving as anchors for adjacent components or as limiters for axial movement. In accordance with DIN 705, these rings embody standardized precision in dimensions, material, and manufacturing tolerances, supporting reliability in countless industrial applications.
Set collars are among the fastening elements, which represent a central category within machine elements. Machine elements are components or construction principles that perform identical or comparable tasks across various machines and apparatus and are therefore regularly found in the same or similar execution.
The role of set collars is unshakeable – they maintain the positioning of components on a shaft, catering to alignment and axial load requirements. DIN 705 provides a comprehensive framework to guide the structural integrity, material quality, and engineering precision of set collars.
The precise specifications of DIN 705 dimensions ensure perfect fit compatibility for shafts of various diameters, leading to consistency and efficiency in operational processes.
DIN 705 set collars are categorized into Forms A, B, and C, each tailored with unique features for diverse industrial applications.
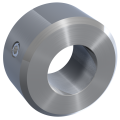
Form A is the simplest variant, which, depending on the size, has one or two threaded holes used for assembly with thread pins DIN EN 27434 (DIN 553) or DIN EN ISO 4027 (DIN 914). These thread pins are pre-assembled and included in the scope of delivery.
The thread pins are screwed onto the shaft, ensuring a secure fixation.
Form B has the same dimensions as Form A but exclusively features a full hole for mounting the set collar with a grooved pin DIN EN ISO 8744 (DIN 1471) or tapered pin DIN EN 22339 (DIN 1), which are not included in the scope of delivery. This type offers a simple and effective solution for many applications where a component needs to be securely and precisely positioned on a drilled shaft. Form B thus prevents the set collar from rotating on the shaft.
Form C offers a combination of the features of Forms A and B.
Thus, it has one or two threaded holes (depending on the size) for assembly with thread pins DIN EN 27434 (DIN 553) or DIN EN ISO 4027 (DIN 914) (pre-assembled included in the scope of delivery) and additionally features a predefined hole for use with a grooved pin DIN EN ISO 8744 (DIN 1471) or tapered pin DIN EN 22339 (DIN 1) (not included in the scope of delivery).
This design allows for a more uniform distribution of clamping pressure on the shaft while simultaneously offering precise positioning of the set collar. Form C is typically used in applications where finer control over positioning and a secure connection with the shaft are required. Therefore, set collars Form C are preferably used in applications where vibrations or torques occur.
Another major advantage of Form C over Form B lies in the comparatively simple assembly, as the thread pins serve as a guide for positioning the set collar during the drilling of the pin hole.
The selection of materials presented in the detailed product tables in the eShop includes various steel grades, each offering robust endurance against different operational challenges – be it installation environment or mechanical stress. For corrosive environments or cases requiring non-magnetic attributes, the choice of material proves crucial.
The merits of using DIN standard-compliant set collars multiply through their standardized composition, which enhances interchangeability, simplifies maintenance, thereby reducing the likelihood of machinery downtime. The applications of set collars span various industries and stand as a testimony to the adaptability of this component.
2. Product details (form A / form B / form C)
Form A
Size: 2 – 150
Material: Automatic steel, stainless steel
Surface: plain, white galvanically zinc plated
Bore tolerance: H8
With thread pin (already assembled)
- up to size 70 with one thread pin (up to M10 with slot according to DIN EN 27434 (DIN 553) and from M12 with hexagon socket according to DIN EN ISO 4027 (DIN 914)
- from size 75 with two thread pins with hexagon socket according to DIN EN ISO 4027 (DIN 914)
Outer diameter strongly chamfered on one side
Form B
Size: 2 – 200
Material: Free-cutting steel, Stainless steel
Surface: plain, white galvanized
Hole tolerance: H8
With a complete hole for mounting with a grooved pin DIN EN ISO 8744 (DIN 1471) or taper pin DIN EN 22339 (DIN 1) (not included in the delivery)
Outside diameter chamfered on one side
Form C
Size: 2 – 150
Material: Free-cutting steel, Stainless steel
Surface: plain, white galvanized
Hole tolerance: H8
With a thread pin (already assembled) and a hole for use with a grooved pin DIN EN ISO 8744 (DIN 1471) or taper pin DIN EN 22339 (DIN 1) (not included in the delivery)
- up to size 70 with a thread pin (up to M10 with slot according to DIN EN 27434 (DIN 553) and from M12 with hexagon socket according to DIN EN ISO 4027 (DIN 914)
- from size 75 with two thread pins with hexagon socket according to DIN EN ISO 4027 (DIN 914)
Outside diameter chamfered on one side
Form B
Size: 2 – 200
Material: Free-cutting steel, stainless steel
Surface: bright, white galvanically zinc plated
Bore tolerance: H8
With complete bore for assembly with grooved pin DIN EN ISO 8744 (DIN 1471) or taper pin DIN EN 22339 (DIN 1) (not included in the delivery)
Outer diameter strongly chamfered on one side
Form C
Size: 2 – 150
Material: Free-cutting steel, stainless steel
Surface: bright, white galvanically zinc plated
Bore tolerance: H8
With threaded pin (already mounted) and a bore for use with grooved pin DIN EN ISO 8744 (DIN 1471) or taper pin DIN EN 22339 (DIN 1) (not included in the delivery)
- up to size 70 with one threaded pin (up to M10 with slot according to DIN EN 27434 (DIN 553) and from M12 with hexagon socket according to DIN EN ISO 4027 (DIN 914))
- from size 75 with two threaded pins with hexagon socket according to DIN EN ISO 4027 (DIN 914)
Outer diameter strongly chamfered on one side
3. Areas of Application & Compatibility
Applications of DIN 705 set collars
The use of DIN 705 set collars extends well beyond the boundaries of a single industry and illustrates their indispensable role within the industry. These rings embody a crucial element of application function and safety.
In sectors such as heavy industry – an area that encompasses mining, manufacturing, and construction – the use of steel set collars within machinery is fundamental to prevent component displacement. A key factor in compliance with processes.
Precision applications demand the reliable accuracy of DIN 705 set collars. The mechanical components maintain the balance of gears, bearings, and sprockets with strict precision, prevent equipment malfunctions, and increase the lifespan of machines.
Automation areas tend towards adjustable set collars because of their ability for quick readjustment during changes or maintenance work. The clear design of the DIN 705 set collar form A facilitates rapid adjustments without compromising the anchoring of the shaft, a trait valued by engineers who rely on the reliability of DIN 705 for consistent shaft alignment and uniform rotation.
Compatibility of shaft size and precision
The first step is to ensure that the inner diameter of the set collar matches the specific diameter of your shaft to ensure a precise and secure fit. Use the dimensions for DIN 705 in the eShop to check this compatibility.
Lastly, the practical application is a crucial factor. If regular changes or disassembly are expected, set collars that offer adjustability are of great benefit.
Ultimately, a precise selection process requires understanding the dimensional requirements, examining operational loads, considering environmental resistances, and being aware of specific application regulations. Adhering to the specifications for DIN 705 is crucial for a successful choice.
4. Benefits and Advantages
Precise standards
Compliance with standards: DIN 705 sets precise requirements for the dimensions, tolerances, and material qualities of set collars. This ensures users that the products are compliant and of high quality.
Compatibility: Through standardization, high compatibility with various shafts, components, and systems is ensured.
Quality and Reliability
Material quality: Set collars according to DIN 705 are made from high-quality materials, providing durability and resistance to mechanical stresses and corrosion.
Reliable fastening: They allow for a secure and reliable fixation of components on shafts, thereby preventing vibration, displacements, and potential damages.
Versatility
Application diversity: Set collars can be used in a wide range of applications, including mechanical engineering, plant construction, and many more.
Adaptability: The availability of different sizes and types allows for flexible adaptation to specific requirements and operating conditions.
Economy
Easy assembly and disassembly: Set collars are easy to install and remove when necessary, simplifying maintenance and exchange work.
Cost savings: The use of set collars can contribute to reducing machine downtime and repair costs, as they provide an effective solution for positioning and securing components.
Safety
Increasing operational safety: Precise fixation of components can minimize accidents and failures that could be caused by unintended movements of parts.
Protection of critical components: Set collars help to extend the lifespan of machines and equipment by ensuring correct positioning and minimizing wear. Overall, set collars according to DIN 705 provide a reliable and efficient solution for positioning and securing components, leading to improved performance, safety, and longevity of facilities and machines.
5. Assembly and Installation
Preparation
- Check the shaft: Make sure before assembly that the shaft is clean, free from damage and burrs. A smooth surface ensures a good fit and function.
- Select the right set collar: The set collar must match the diameter of the shaft on which it is to be mounted.
Assembly steps
- Positioning the set collar: Slide the set collar to the desired position on the shaft. If you are mounting several set collars, make sure they are placed in the correct order and orientation.
- Orientation: Make sure that the opening of the set collar, if present, points in the desired direction. Threaded hole, bore, or hole should be easily accessible.
- Tightening the grub screws, setting the cotter pins/taper pin: Use the appropriate flat-head screwdriver or Allen key to tighten the set collar's grub screw. Tighten the grub screw evenly until the ring is securely attached to the shaft and can no longer move. Be careful not to exceed the torque to avoid damage to the shaft or set collar.
Set collar versions with bore are precisely positioned with a cotter pin or taper pin. Insert the cotter pin or taper pin by hammering. Make sure that a bore is pre-drilled on the shaft and the hole is drilled according to the nominal diameter of the pin. - Inspection: After tightening, check whether the set collar is securely seated and the position of the attached component is correct. Ensure that there is no movement along the shaft or unintended looseness.
Important: For safety reasons, appropriate measures must be taken during the final assembly of the threaded, cotter, or taper pins to ensure that the pins do not protrude.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What are the main functions of DIN 705 set collars?
What material are DIN 705 set collars made of?
Which standard regulates the properties of set collars?
DIN 703 includes set collars of the heavyweight series and DIN 705 set collar of the light series.
Why is the choice of the right material for set collars crucial?
What role does installation play for DIN 705 set collars?
How is a secure shaft connection guaranteed by DIN 705 set collars?
What distinguishes DIN 705 set collars from set collar types according to DIN 703?
Set collars according to DIN 703 (heavy series) are more massive than those according to DIN 705 (light series).
What advantages do stainless steel set collars offer compared to those made of automatic steel?
How does one determine the correct size of a set collar?
Can DIN 705 set collars be attached to already mounted shafts – without dismantling the shaft?
Are special tools required for the installation of DIN 705 set collars?
How does the standardization of set collars contribute to efficiency in production?
Can DIN 705 set collars be used in dynamic applications?
Are DIN 705 set collars reusable?
How is quality control conducted in the manufacturing of DIN 705 set collars?
Are set collars and clamp collars the same?
Set collars are primarily used to position or secure a component on a shaft. They have one or more screws with which they are clamped to the shaft. Their main function is to prevent the component from moving along the axis of the shaft. Set collars offer a simple but effective solution for applications where precise positioning is required.
Clamp collars, on the other hand, are known for their ability to establish a connection between two components, such as a shaft and a shaft pin or a shaft and another component. Unlike set collars, which primarily have a positioning function, clamp collars can transfer forces. They are tightly clamped around the shaft and can absorb both axial and radial loads. In summary: Set collars are primarily responsible for positioning, while clamp collars can also transfer forces and connect components.
What are the differences between DIN 705 form A vs. form B and C?
DIN 705 set collars are categorized into form A, B, and C, each tailor-made with unique features for diverse industrial applications.
Form A is the simplest variant, which depending on the dimensions, has one or two threaded holes, used for installation with set screws DIN EN 27434 (DIN 553) or DIN EN ISO 4027 (DIN 914). These set screws are pre-assembled and included in the delivery.
The set screws are screwed onto the shaft to ensure secure locking.
Form B has the same dimensions as form A, but is exclusively equipped with a full bore for mounting the set collar with a grooved pin DIN EN ISO 8744 (DIN 1471) or taper pin DIN EN 22339 (DIN 1), which are not included. This type offers a simple and effective solution for many applications where a component needs to be securely and precisely positioned on a drilled shaft. Thus, form B prevents the set collar from rotating on the shaft.
Form C offers a combination of the features of form A and B.
Therefore, it has one or two threaded holes (depending on size) for mounting with set screws DIN EN 27434 (DIN 553) or DIN EN ISO 4027 (DIN 914) (pre-assembled in the delivery) and additionally a predefined hole for use with a grooved pin DIN EN ISO 8744 (DIN 1471) or taper pin DIN EN 22339 (DIN 1) (not included).
This design allows for a more uniform distribution of clamping pressure on the shaft and at the same time offers precise positioning of the set collar. form C is typically used in applications where finer control over positioning and a secure connection to the shaft are required. Therefore, set collars form C are preferably used in applications where vibrations or torque occur.
Another major advantage of form C compared to form B is the comparatively simple assembly, as the set screws serve as an aid to fix the set collar when drilling the pin hole.
Are set collars also custom made to measure?
If you already have a drawing of your desired part or would like to develop a solution together with us, do not hesitate to directly contact mbo Oßwald. We are ready to turn your ideas into reality.